How is this drug name pronounced?
Ado-trastuzumab emtansine: A-doh-tras-TOO-zoo-mab em-TAN-seen
Kadcyla: kad-SY-luh
What cancer(s) does this drug treat?
Kadcyla is approved for:
Advanced breast cancer
- Patients with advanced breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body and that tests positive for the HER2 molecule, who have previously received trastuzumab (Herceptin) and taxane chemotherapy (separately and in combination). Patients should have either received prior treatment for their advanced disease, OR had their disease come back after receiving treatment for their early disease.
Early breast cancer
- Patients with early breast cancer that tests positive for the HER2 molecule, who had received taxane chemotherapy and a trastuzumab (Herceptin)-based treatment prior to surgery, but have cancer cells remaining around the tissue that was removed during surgery. In this case, Kadcyla is used as an adjuvant (after surgery) treatment.
Limitations of use:
Age: The safety and efficacy of Kadcyla in patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Fertility/Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Kadcyla may impair fertility in both women and men. Kadcyla can result in the death of the fetus and can cause birth defects. Women should use effective contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Kadcyla and for at least seven months after the last dose of Kadcyla. Men should use effective contraception during treatment with Kadcyla and for at least four months after the last dose of Kadcyla. Kadcyla may cause serious adverse reactions to the breastfed child. Women are advised not to breastfeed during treatment with Kadcyla and for at least seven months after the last dose of Kadcyla.
Interactions with other drugs: Administration of Kadcyla at the same time as strong CYP3A4 inhibitors should be avoided.
What type of immunotherapy is this?
- Antibody-drug conjugate
How does this drug work?
- Target: HER2
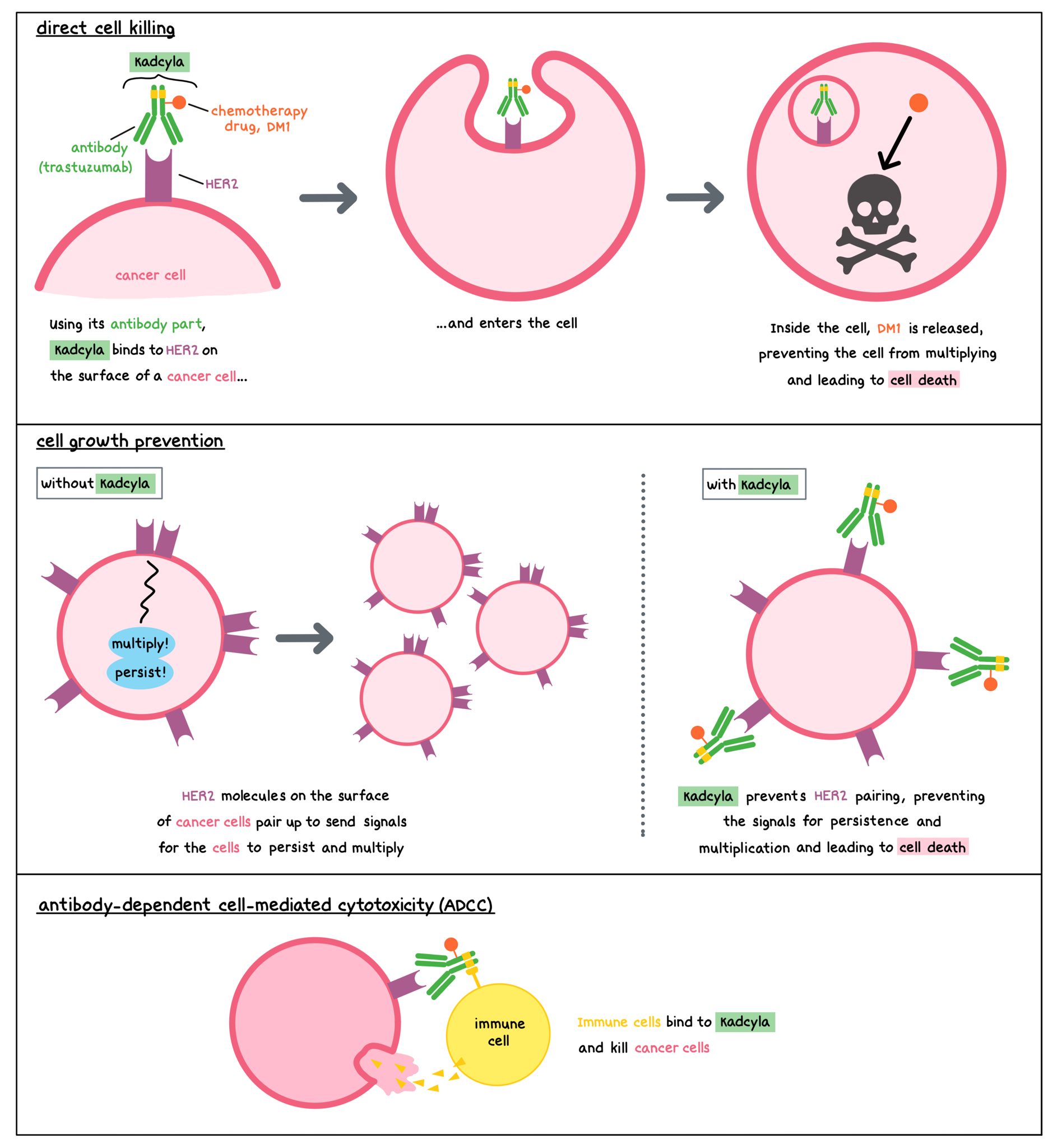
Kadcyla is a medicine that consists of two parts that are connected: an antibody called trastuzumab that attaches to a molecule called HER2 on the surface of cancer cells, and a chemotherapy drug called DM1. HER2 is a protein present on the surface of different types of healthy cells, and it plays a role in regulating the multiplication and survival of cells. HER2 is also found in higher quantities on the surface of some breast cancer cells.
Trastuzumab and other antibody molecules have an overall “Y” shape. The two tips of the upper arms of the “Y” shape are the parts of the antibody that can very precisely bind to their target. The stem of trastuzumab’s “Y” shape can attract immune cells or other parts of the immune system.
Kadcyla works to kill breast cancer cells in at least three ways.
Direct cell killing
By targeting HER2, Kadcyla is designed to minimize harm to normal, healthy cells and to bring the chemotherapy directly to the cancer cells. Kadcyla is designed to bring the chemotherapy directly to the cancer cells in a targeted way, and to minimize harm to normal, healthy cells. When Kadcyla binds to HER2, it can enter the cell it is bound to. Inside the cell, the chemotherapy part of Kadcyla is released and causes the cancer cell to die. This is understood to be the main way through which Kadcyla kills cancer cells.
Cell growth prevention
Without Kadcyla, HER2 molecules on the surface of cancer cells pair up to send signals that ensure the cells’ survival and encourage the cells to multiply. By binding to HER2, Kadcyla blocks these signals and prevents the cancer cells from persisting and multiplying.
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
When bound to HER2 on the surface of cancerous cells, the “stem” of the antibody part of Kadcyla can also attract and bind immune cells (like NK cells). This allows Kadcyla to act as a bridge between the target cell and the immune cell. The immune cell then releases molecules that can kill the cell Kadcyla is bound to.
How is this drug given to the patient?
Kadcyla is administered via a tube into a vein (intravenous infusion, or i.v.) every 3 weeks. The first infusion is administered over 90 minutes. If the first infusion is well tolerated, subsequent infusions are administered over 30 minutes. The total number of infusions depends on the indication and how well the patient responds to the treatment.
What are the observed clinical results?
For:
Advanced breast cancer
Early breast cancer
It is important to keep in mind that each patient’s actual outcome is individual and may be different from the results found in the clinical studies. In addition, with immunotherapy, sometimes it takes several months for responses to be observed.
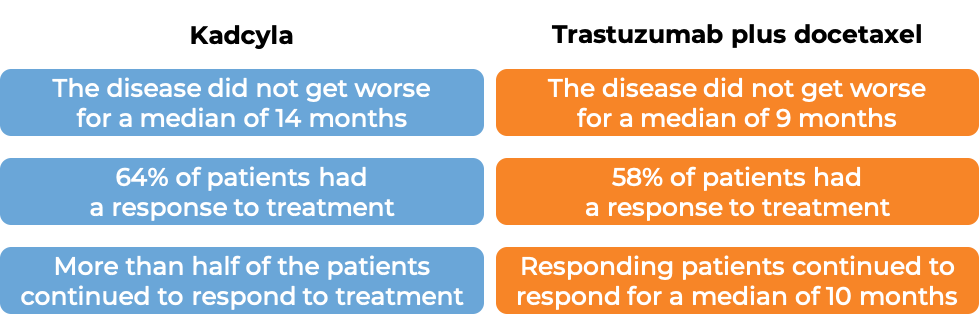
Advanced breast cancer
In a clinical trial, 991 patients with advanced breast cancer that had either grown within the breast and could not be removed by surgery or had spread to other parts of the body, and had tested positive for the HER2 molecule, and who had received prior taxane chemotherapy and trastuzumab (Herceptin)-based treatment for their disease, were treated with either Kadcyla OR chemotherapy (lapatinib plus capecitabine). At a median treatment duration of 6 months for Kadcyla and 5 months for chemotherapy and a median follow-up of 13 months:

Early breast cancer
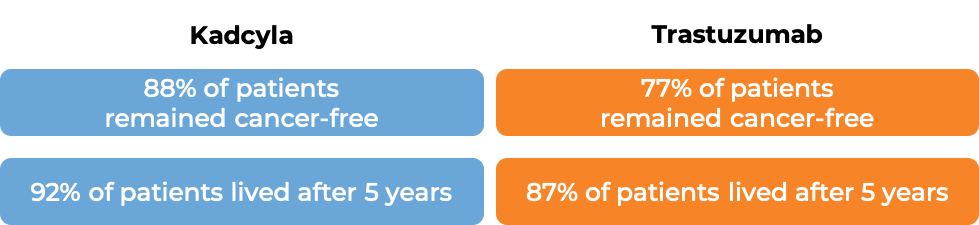
In a clinical trial, 1486 patients with early breast cancer that had tested positive for the HER2 molecule, who had received taxane chemotherapy and a trastuzumab (Herceptin)-based treatment prior to surgery, and had cancer remaining around the tissue that could not be removed during surgery, were treated with either Kadcyla or trastuzumab.
After 3 years, 87% of patients receiving Kadcyla remained cancer-free, while 77% of patients receiving trastuzumab remained cancer-free.
What are the side effects?
The most common side effects of Kadcyla include tiredness; nausea; pain in the bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and joints; headache; liver problems; nose bleeds; bleeding, low platelet count; constipation; and weakness, numbness, and pain in the hands and feet.
Kadcyla can cause side effects that can become serious or life-threatening, and may lead to death. Some of the serious side effects related to Kadcyla include severe problems with the liver, heart, and lungs; difficulty breathing; serious bleeding; low platelet count; nerve damage; infusion-related reactions; and hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions to Kadcyla.
Patients should report any symptoms to their healthcare provider, who can then initiate actions to limit or reverse the side effects. For a more complete list of possible side effects, see the full prescribing information.
Additional information
Manufacturer
US: Genentech Europe: Roche
Approval
FDA and EMA
Links to drug websites
- US: https://www.kadcyla.com/
- Europe: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/kadcyla
Other references
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejmoa1209124
Last updated August 11, 2025