How is this drug name pronounced?
Aldesleukin: AL-des-LOO-kin
Proleukin: proh-LOO-kin
What cancer(s) does this drug treat?
Advanced kidney cancer
Proleukin is approved for:
- Patients with renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer) that has spread to other parts of the body.
Advanced melanoma
Proleukin is approved for:
- Patients with melanoma that has spread to other parts of the body.
Limitations of use:
Age: The safety and efficacy of Proleukin in patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Exclusions: Proleukin should not be administered to patients with abnormal heart, lung, kidney, liver, or central nervous system functions. Proleukin should not be administered to patients with brain metastases (cancer that has spread to the brain). Proleukin should not be administered to patients who have received an organ transplant (allograft). If patients develop severe sleepiness, continued treatment with Proleukin may result in a coma, and thus should be discontinued.
Fertility/Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Proleukin can cause harm to a mother and fetus, and is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Patients who can become pregnant should use effective contraception during treatment with Proleukin. The risks associated with Proleukin during breastfeeding are not known and cannot be ruled out. Due to the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, the benefits of breastfeeding and the mother’s need for treatment should be weighed accordingly before moving forward with treatment with Proleukin.
Interaction with other drugs: Proleukin may affect the function of the heart, lung, kidney, liver, or central nervous system. Further damage can occur following administration of associated drugs (e.g., narcotics, analgesics, antiemetics, sedatives, tranquilizers, doxorubicin, aminoglycosides, indomethacin, cytotoxic chemotherapy, methotrexate, asparaginase), which can also affect these organ systems. Proleukin treatment can reduce the kidney and liver function of patients. This may delay clearance of associated medications from the body and may increase the risk of harmful side effects from those drugs. Use of glucocorticoids may interfere with the cancer-fighting functionality of Proleukin. Proleukin may induce delayed side effects in patients who are later administered radiographic iodinated contrast media. Additionally, dose adjustments may become necessary for patients treated with certain CYP substrates to prevent toxicity during treatment with Proleukin.
What type of immunotherapy is this?
- Immunomodulator
How does this drug work?
- Target: Interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor
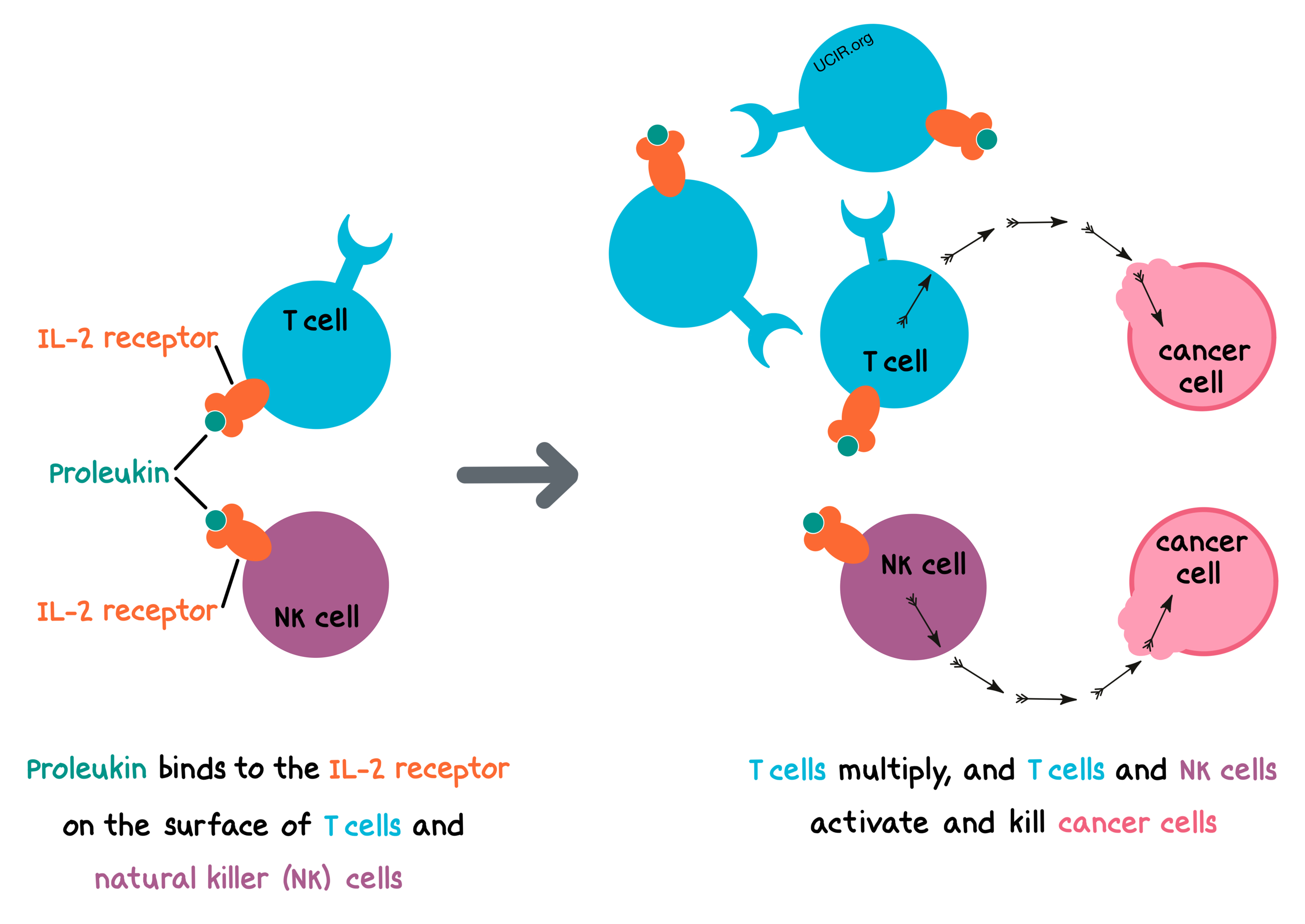
Proleukin is a protein that is a laboratory-made version of interleukin-2 (IL-2) – a protein that naturally exists in the human body. IL-2 is a type of protein called a cytokine. Cytokines are an important part of “cell signaling”, which is when different cells in the body communicate with one another using chemical signals. IL-2 is produced by some immune cells (such as certain types of T cells), and it binds to the IL-2 receptor, found on the surface of many types of immune cells. The exact mechanism by which Proleukin helps fight cancer is not known. It is thought to:
- signal T cells to multiply, extend their lifespan, and enhance their ability to kill target cells like cancer cells,
- activate natural killer (NK) cells to eliminate their target cells, such as cancer cells, and
- generally activate the immune system and prompt the release of various other cytokines.
How is this drug given to the patient?
Proleukin is administered via a tube into a vein (intravenous infusion, or i.v.) over two 5-day cycles that are separated by approximately 9 days of no treatment, and requires a hospital stay. During each 5-day cycle, Proleukin is administered over 15 minutes every 8 hours, for a maximum of 14 doses. Just prior to and during treatment with Proleukin, patients receive a medication to reduce fever, and a medication to treat gastrointestinal irritation and bleeding. Patients may also be treated with antibiotics prior to and during treatment with Proleukin to prevent bacterial infections. Additional medications may be needed to treat other side effects, if they arise.
Prior to beginning treatment with Proleukin and then daily during drug administration, patients get chest x-rays and blood work done, including blood tests for kidney and liver function. The patient’s vital signs (temperature, pulse, blood pressure, and respiration rate), weight, and fluid intake and output are also monitored daily during Proleukin treatment. In addition, patients undergo a thorough assessment of the condition of their heart and lungs before starting, and during treatment with Proleukin.
What are the observed clinical results?
It is important to keep in mind that each patient’s actual outcome is individual and may be different from the results found in the clinical studies. In addition, with immunotherapy, sometimes it takes several months for responses to be observed.
Advanced kidney cancer
In a clinical trial, 255 patients with renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer) that had spread to other parts of the body were treated with Proleukin.
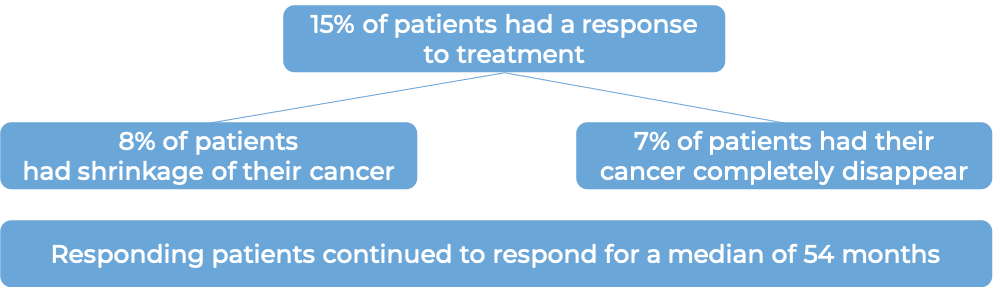
(For the definition of “median”, click HERE.)
Advanced melanoma
In a clinical trial, 270 patients with melanoma that had spread to other parts of the body were treated with Proleukin.
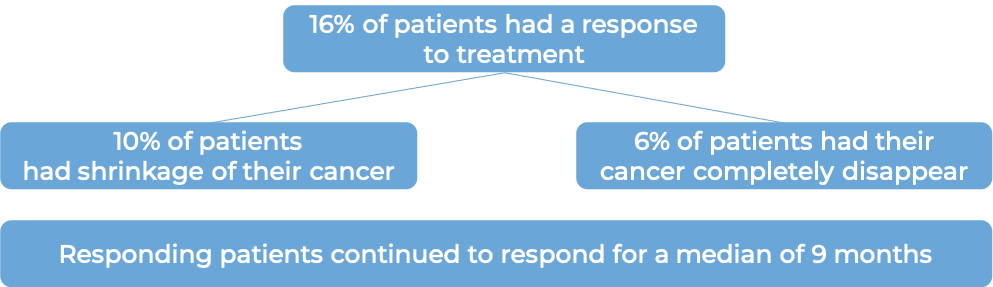
(For the definition of “median”, click HERE.)
What are the side effects?
The most common side effects of Proleukin include low blood pressure, excessive bilirubin in the blood (causing yellowing of the skin and eyes [jaundice]), difficulty breathing, rash, diarrhea, decreased or no urine, chills, vomiting, low platelets in the blood (reduced clotting), nausea, confusion, and high levels of creatinine in the blood (indicating dehydration or kidney dysfunction).
Proleukin can cause side effects that can become serious or life-threatening, and may lead to death. Some of the serious side effects related to Proleukin include decreased or no urine, kidney toxicity or sudden kidney failure, , capillary leak syndrome, neurologic toxicities (which can result in confusion, severe sleepiness, severe mental illness, and coma), serious infections (including in the blood/sepsis), or hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions. Proleukin can trigger or increase autoimmune or inflammatory disorders, such as Crohn’s disease, inflammatory arthritis, and diabetes mellitus.
Capillary leak syndrome
Proleukin can cause capillary leak syndrome (CLS), which begins immediately upon the initiation of treatment with Proleukin. During CLS, proteins and fluid leak out of blood vessels into the surrounding tissues. This could lead to dangerously low blood pressure, which can result in organ failure and death if left untreated. Symptoms that could signal the onset of CLS include fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, extreme thirst, and sudden increase in body weight.
Patients who have been treated with Proleukin may experience unusual reactions to iodinated contrast media, which is used to visualize vessels and changes in tissues radiography and CT.
Patients should report any symptoms to their healthcare provider, who can then initiate actions to limit or reverse the side effects. For a more complete list of possible side effects, see the full prescribing information.
Additional information
Manufacturer
Ivovance biotherapeutics
Approval
FDA
Links to drug websites
Last updated: October 20, 2025


